Not in the mood to read? Check out the summary video here.
The SWOT Analysis is an essential part of any business strategy discussion. It allows companies to evaluate their strengths and weaknesses and potential opportunities and risks from outside sources.
This post will examine the key examples of threats in a SWOT analysis. Knowing the risks businesses typically deal with can help you better handle the intricate internal and external issues you may face.
Key Takeaways
- Businesses must adapt to technology disruption to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
- Economic downturns can significantly impact businesses, necessitating strategic planning and preparation.
- Changing consumer habits, driven by online shopping and the desire for unique experiences, require businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Cybersecurity breaches pose a serious threat to businesses, leading to data loss, reputation damage, and financial losses.
- Legal and regulatory changes can impact various aspects of businesses, requiring them to stay informed and adaptable.
- Intense competition can lead to price wars, loss of market share, and concentration.
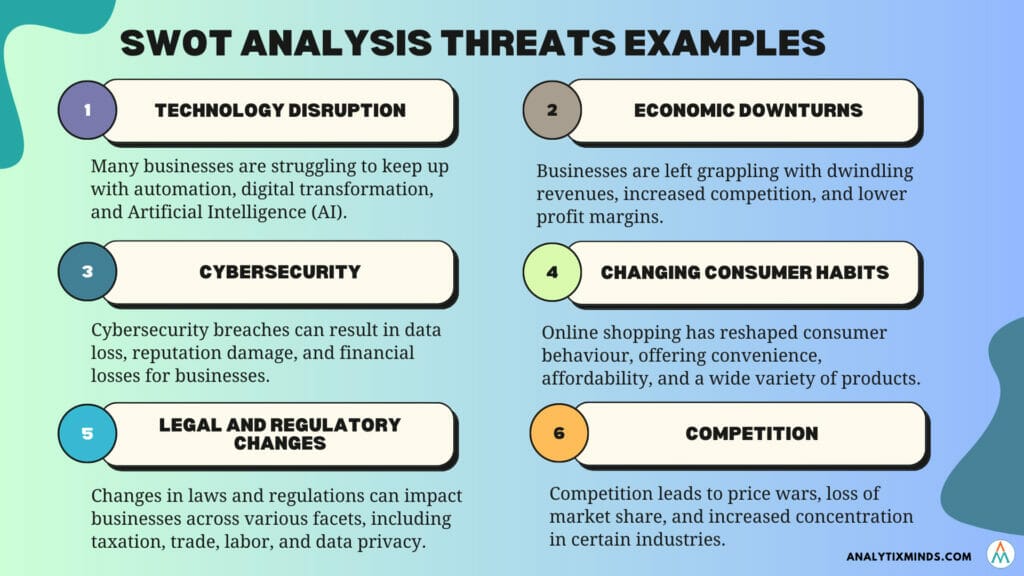
Table of Contents
Examples of Threats in a SWOT Analysis
Summary Video
Technology Disruption
In the past, Automation was the silver bullet that helped businesses reach more customers swiftly and drastically cut costs by eliminating manual labour and time-intensive tasks. In the new millennium, there have been other technology-driven disruptions.
The Digital Globalization
Digital globalization has completely reshaped the global economy. It has been the magic wand that has opened up new markets and customer bases for businesses. Smaller economies and enterprises have been able to enter international trade with specialized products and services.
The explosion of global data flows, thanks to near-zero marginal costs of digital communications and transactions, has made it a breeze for customers to order goods online, track their movement, and pay online.
It all became possible with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and other interconnected business applications that have become cheaper to implement for a business of any size.
The Covid-19 Pandemic and the Digital Adoption Surge
There’s no denying the Covid-19 pandemic has changed the way we live, work, and interact. Digital transformation was already underway before the virus hit, but it’s accelerated at an unprecedented rate since then.
Consumers have embraced online channels for shopping and services; businesses are rapidly transitioning to digital customer interactions; organizations have had to fast-track digitally enhanced offerings – all due to the digital adoption surge driven by Covid-19.
The impact on businesses is staggering: over 80% of customer interactions now occur digitally. Companies have had to pivot and focus their product portfolios toward improving user experience via digital tools such as mobile apps and websites.
We all experienced how many big-name restaurants struggled at the height of the pandemic to transition to online ordering and contactless delivery.
Those businesses that made this change swiftly were able to somewhat minimize the damage.
Investments in data security measures and cloud migration strategies have become vital for any business wishing to stay competitive in this period. Simultaneously, physical footprints have significantly decreased, with many offices transforming into virtual workspaces overnight – a change few people thought would happen so rapidly.
So, as you already know, the Tech Disruption is real. In the race to stay in business, companies need to constantly innovate. Businesses need to double down on understanding customer needs through big data analytics to fine-tune their products or services. Failure to do so may result in missed opportunities in an already saturated marketplace where differentiation is minimal.
Economic downturns
From the thrill of the ascent to the precipitous drop, an economic cycle often feels like a roller coaster ride. When the descent happens – the so-called economic downturn or recession – it instills a sense of unease and uncertainty among businesses and individuals alike.
It is highly likely that your employer or a company you knew probably laid-off employees and downsized their operations during a recession.
The Ripple Effect of Economic Downturns
During an economic downturn, consumer spending habits can shift dramatically, often leaning towards necessities over luxuries. Businesses, particularly smaller ones, can be left grappling with dwindling revenues, increased competition, and lower profit margins.
Additionally, downturns can lead to a rise in operational costs, impacting the supply chain and availability of business financing options.
Unravelling of the Corporate Titans during the 2008 Crisis
During the 2008 financial crisis, several giant corporations faced severe consequences. Lehman Brothers, a leading investment bank, was forced to file for bankruptcy in September 2008. This resulted in the loss of billions in investments and widespread unemployment.
Lehman Brothers had $639 billion in assets but $613 billion in debt and filed for bankruptcy in September 2008.
Bear Stearns, another Wall Street firm, narrowly avoided the same fate due to an acquisition deal with JP Morgan Chase facilitated by the US government.
The auto industry was also affected, with General Motors Corporation undergoing a significant restructuring that resulted in plant closures and extensive layoffs.
The strategic significance of anticipating downturns
These examples underscore the devastating impact of economic downturns. Even established corporations can face significant challenges when liquidity dwindles, and consumer confidence drops.
Strategic planning must account for the potential of economic downturns – a risk factor that can’t be overlooked.

Changing Consumer Habits
The online shopping revolution is here, reshaping consumer behaviour like never before. The comfort, affordability, and sheer variety of e-commerce have catapulted it to the forefront of retail. But what’s driving this change forward?
The Dawn of Shopping Comfort
Remember the days of leaving home at dawn and standing in a long line on boxing day just to get your hands on that one item? Well, you can still do that this year. However, you can now buy from the comfort of your couch from most retailers and have it delivered to your doorstep, even during Black Friday or Boxing Week. So, as a business, you have to strategize how your online shopping experience and delivery service can be streamlined.
The New Retail Battlefield
The low overhead costs of online businesses mean cheaper products and more savings in the consumer’s pocket. Add the fierce competition among digital vendors to the mix. To stay in the game, businesses must keep a sharp eye on pricing trends and adjust their strategies.
Mobile E-commerce
The rise of mobile commerce has put shopping on the wings. With smartphones and tablets, consumers can shop anytime, anywhere. For businesses, it’s time to ensure your websites are mobile-friendly and tap into location-based marketing.
In the US alone, it is projected to have 266 million online shoppers in 2023. And 65% of digital shoppers use their mobile devices for online shopping.
The Shift in Consumer Preferences
Forget collecting things. It’s all about collecting experiences now. This shift is evident across industries, especially in travel and tourism. Today’s social media-savvy consumers are looking for unique, photo-worthy experiences over luxury possessions.
As a decision-maker, you better keep a pulse on changing consumer behaviours and adapt in real time. The pandemic has fast-tracked the adoption of online shopping and home exercising, making it crucial for businesses to adjust their strategies.
Home Fitness: Exercising in the Comfort of Home
The pandemic has also spurred a fitness revolution at home, with more people turning to at-home workouts. Businesses in health and wellness should focus on providing digital wellness products and services.
The home fitness and equipment industry grew more than 25.10% to $10.18 billion in 2020. It is projected to be worth anywhere from $14.74 to $21.13 billion by 2028.

Cybersecurity
The relentless threat of cybersecurity breaches has been around for some time. These digital disruptions hold the potential for far-reaching consequences, including data losses, reputational damage, monetary strain, legal repercussions, and operational chaos.
In this section, let’s see why cybersecurity should be a key part of SWOT analysis in any organization with a digital footprint.
Data Loss (The Silent Tsunami)
Data loss may be the most nefarious and damaging result of a cybersecurity breach. This silent tsunami can cripple customer service, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property protection.
According to cybersecurity gurus at Risk Based Security (RBS), an astonishing 37 billion records slipped through the cracks and into the wrong hands in 2020, all because of cybersecurity breaches.
The exposure of sensitive information such as personal data, credit card details, login credentials, and trade secrets can open Pandora’s box, leading to identity theft, scams, blackmail, or even espionage.
Reputation Damage
Cybersecurity breaches can cause a company’s reputation to plummet faster than a video going viral on TikTok. Data leaks can erode customer trust and loyalty, sour relationships with stakeholders and investors, and even jeopardize partnerships with suppliers.
An IBM survey unveiled that 75% of consumers would shun a company they perceive as incapable of safeguarding their data. This reputational damage can negatively impact a brand’s value, market position, customer base, and potential for revenue growth.
Financial Losses
The financial repercussions of cybersecurity breaches are another significant, often overlooked fallout. The immediate costs, such as containment and recovery expenses, regulatory fines, and legal compensation, can be astronomical.
But there are also indirect costs to consider: lost business opportunities, increased insurance premiums, ballooned operating costs, and reduced productivity.
According to IBM’s 2020 Cost of Data Breach Report, the average global cost of a data breach was a wallet-emptying USD 3.86 million.
Strategies to Manage Cybersecurity Risks
Given these potentially catastrophic implications, it’s crucial to proactively anticipate and mitigate these cyber threats. Here are some best strategies for tackling cybersecurity risks head-on:
- Regularly conduct risk audits to identify potential weaknesses and threats lurking in your digital shadows.
- Establish security protocols and procedures that align with industry standards and best practices, like the gold-standard ISO 27001 or the comprehensive NIST SP 800-53.
- Educate your employees on cyber safety habits, from crafting robust passwords and avoiding phishing emails to updating software patches and reporting suspicious activities.
- Implement security tools such as antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, and data backup solutions to fortify your data fortress against unauthorized access or manipulation.
- Keep a vigilant eye on network activity for signs of intrusion or anomalies using tools like SIEM or IDS/IPS.
- Respond swiftly and decisively to security incidents with a well-defined incident response plan, complete with roles, responsibilities, procedures, and communication channels.

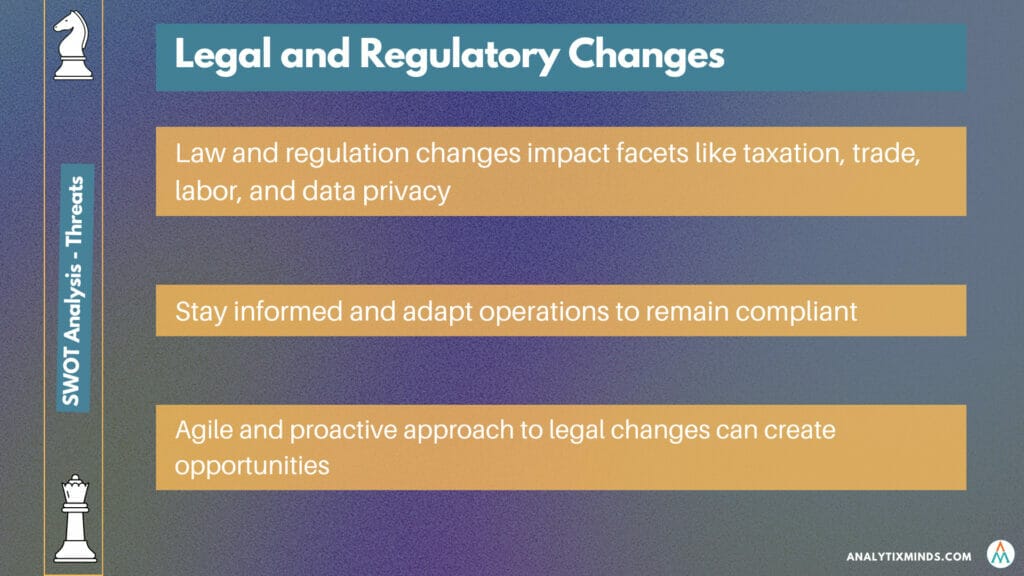
Legal and Regulatory changes
The complex web of laws and regulations is constantly shifting, mirroring societal needs, emerging challenges, and new opportunities. This means businesses must stay attuned to the legal and regulatory climate affecting their operations, offerings, customers, employees, and stakeholders.
Impact of Legal and Regulatory Flux on Businesses
Changes in laws and regulations can come from various government tiers – national, state/provincial/territorial, local – or international bodies (like the World Trade Organization) or regional alliances (such as the European Union).
They can ripple across various business facets, including taxation, trade, labour, health and safety, environmental conservation, data privacy and security, consumer rights, and competition law.
Here are some examples of how legal or regulatory changes can shape businesses:
Tariffs and trade policies
Tweaks in global trade policies can touch businesses that export and import goods or dabble in foreign direct investments. For instance, trade policies often tighten the reins on business activities in China.
Paid sick leave and minimum wage
Changes in labour laws can sway employee hiring and retention costs, as well as morale, productivity, and turnover. Some regions, for example, require employers to offer paid sick leave to employees.
Sales tax
Shifts in sales tax rates or rules can affect businesses’ revenue, profit margins, customer demand, and pricing strategies. Some regions, for instance, have begun taxing digital products or services.
Federal tax policy
Amendments to federal tax laws can reshape businesses’ tax obligations and incentives, investment decisions, and cash flow. For instance, the US Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 cut the corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21%.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Evolutions in data privacy and security laws can redefine businesses’ compliance requirements and risks, as well as customer trust and loyalty. The GDPR, for instance, imposes strict rules on how companies handle the personal data of EU citizens.
Affordable Care Act (ACA)
Overhauls in healthcare laws can impact businesses’ health insurance costs, benefits, and employee well-being. The ACA, for example, mandated most employers to provide health insurance coverage to full-time employees or risk a penalty.
The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021
Changes in stimulus packages can affect businesses’ financial relief and support, as well as economic recovery and growth. For example, the American Rescue Plan Act earmarks $1.9 trillion in aid for individuals, businesses, and regions.
The Obstacles Paved by Legal and Regulatory Changes for Businesses
Ramping up costs or complexity
Legal or regulatory shifts can pile on extra costs or requirements, making it more challenging for businesses to operate or compete. For example, adhering to stricter environmental regulations might necessitate hefty investments in green technologies or processes.
Breeding uncertainty or instability
Legal or regulatory shifts can breed an unpredictable climate, making it tough for businesses to strategize or make informed decisions. Persistent trade disputes or policy changes, for instance, can sow uncertainty about future market conditions or growth prospects.
Curbing growth or profitability
Legal or regulatory shifts can hinder a business’s growth potential or profitability by restricting certain activities or levying additional costs or constraints. Steeper taxes or regulations on specific industries may stunt their growth or profit potential.
Adapting to Legal and Regulatory Shifts
While changes in laws and regulations can pose challenges, businesses that remain adaptable and proactive can still thrive. Regular consultation with legal and industry experts, staying abreast of legislative updates, and fostering a culture of agility and resilience can help businesses navigate the ever-changing legal and regulatory maze.
After all, it’s not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the ones most responsive to change.
The Threat of Competition
Last but not least, let’s look at the biggest threat to any business that’s continuously on everyone’s minds. Companies compete over clients, resources, or market shares every day. It is a continuous tug-of-war between enterprises that serve the same market segment.
Direct competition
Think along the lines of age-old rivalries like Apple iOS vs. Android, Pepsi vs. Coca-Cola, or Netflix vs. Hulu. These giants aim their arrows at similar target audiences, making their face-off fascinating. A recent survey brings to light this battleground, revealing that the average business is elbowing out around 29 competitors – a testament to the aggressive competition across different sectors.
Price Wars
As reported in this article, Price wars can break out in intensely competitive markets, where companies drastically cut their prices to attract customers and expand their market reach. Consider the price tussle between airlines S and Xone. After S Airlines dropped its prices to $500 per trip, Xone Airlines counter-punched by reducing their price to $490. Though this seems to be a win for consumers on the surface, it may inadvertently dent a company’s profit margins/ the quality of service.
Fluctuating Market Shares
A company’s dwindling stake in the market signifies a loss of market share. A business can stumble due to competitors’ entry, offering similar services with competitive pricing or improved features.
Market Concentration
Markets in the United States have progressively become more concentrated, making competition in numerous sectors stagnant. For example, four beef packers dominate over 80% of their market, while four airlines have a stranglehold on domestic air travel. Such market dominance can lead to decreased competition and inflated consumer prices.
Reclaiming Lost Territory
Companies often employ strategies such as changes in pricing, inventive promotions, or product enhancements to regain their lost market share. The objective is to lure back customers and climb up the market ladder.
Competitive Intelligence
About 90% of Fortune 500 companies have an ace up their sleeve – competitive intelligence. This strategy is widely recognized for its potential to give a leg up against business rivals. It’s no wonder that over 73% of businesses feel that competitive intelligence could have boosted their past campaigns’ success.

