Not in the mood to read? Watch the summary video below.
Who qualifies as a critical thinker? It can be difficult to know if you’re using your critical thinking skills when you should be. More importantly, what’s the point of critical thinking? If you think critical thinking is just identifying the best answer from a range of possible answers, you’re not alone.
How to be a critical thinker? First, you must accept that there are multiple perspectives to a given situation before you can become a critical thinker. You must also be observant in order to identify potential problems.
Critical thinking: what does it mean?
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information and form a judgment. This includes being able to identify bias, fallacies, and other forms of errors in reasoning.
An effective solution requires considering a problem from several different angles. In fact, it involves analyzing a problem from multiple perspectives and evaluating it accordingly.
So, critical thinking relies on reasoning, challenging assumptions and remaining objective. You can improve your critical thinking skills if you embrace these key traits discussed in this article.
Table of Contents
Video – Top 7 Tips to be a Critical Thinker
Summary Video – 7 Tips to be a critical thinker
The process of critical thinking involves open-mindedness, observation, and questioning assumptions. When you are a critical thinker, you can make the right decisions and reach the best conclusions.
Critical thinking only happens when you question both the information and your decision. Then you’ll be able to make the right decision.

Consider the following example.
A team of engineers is designing a building. Their extensive knowledge of structural integrity allows them to design buildings that meet all standards. They have already analyzed the spatial rigidity and load-bearing of the tall structure.
The public’s trust in the building designers could be undermined if they don’t also take into account the aesthetics and user experience.
Critically considering these factors outside their domain of expertise is the only way they can design a building that people will feel comfortable and enjoy.
Creativity and critical thinking go hand in hand.
Top skills for a critical thinker
Critical thinking involves observation, logical reasoning, analysis, and inference. All these elements are essential in improving your critical thinking skills.
1. Observation
Critical thinking begins with observation. Pay attention to the details when you notice something. When observing, it is crucial to be as objective as possible and to consider all available informaion.
Observation can help you spot opportunities and solve problems. Finding a method that works for you when it comes to observing is important. It’s up to you whether you take notes or just observe and take mental notes. Thinking critically requires the following basic observation skills.
- Ability to pay attention to detail
- Being aware of your surroundings
- Be able to focus for a long time
- Recalling what you’ve seen or heard
The next step is to analyze the issue or problem. This means you examine it more closely and look for patterns and relationships between the different elements.
2. Analyze
Analysis of information is crucial to becoming a critical thinker. Compare all the data and evidence with your own inferences. For this to work, you must be open-minded so that you can evaluate your hypotheses objectively.
Using analytical skills, critical thinkers can break complex problems or ideas into smaller, more manageable chunks. This is accomplished by skillfully conceptualizing the relationships between the important aspects of the issue.
Brainstorming, mind maps, and flow charts can all be used to accomplish this. When you break down a problem or idea, it’s easier to identify the underlying causes.
3. Inference
An inference is a conclusion derived from evidence and reasoning. Then, using our prior knowledge and experiences, we make inferences to fill in the gaps in our understanding of a situation.
We reason by using the information we already know to make deductions about what we don’t know. To do so, we must first identify the premises or facts and then use our knowledge to determine what logical conclusions can be drawn.
There are two kinds of logical thinking involved in thinking critically.
1. Deductive reasoning
2. Inductive reasoning
Deduction refers to the process of drawing conclusions based on generally accepted information.
For example, when you plan to attend a concert, you may know that getting through the line and getting to your seat will take about an hour or so.
You also know that transit buses run every 30 minutes. You can then determine the time to leave the house to ensure you arrive on time for the concert based on these two facts.
Inductive reasoning, or induction, is to draw conclusions from observations when there is insufficient data to make a logical deduction.
It is a method by which we form a generalization based on what we already know or observe. It is a powerful tool we can use when we don’t know all the facts.
If you observe that many people are carrying merchandise from a particular brand out of a mall, you can infer that a big sale is happening in that store. By observing people’s behaviour, you can learn about the underlying factors driving their behaviour. In this case, the big sale is the underlying factor causing many people to buy merchandise from the store.
However, it is important to remember that an inductive conclusion is only likely, not certain. As you gain more knowledge or different perspectives, you may need to rethink your inductive conclusions to ensure they remain valid.
4. Curiosity
Curiosity plays an important role in generating new ideas and insights. Learning new things can also help you gain a more rounded perspective and understanding of a situation. By doing so, you can come up with more innovative solutions to problems.
In order to think critically, you must develop your questions and explore and think deeply about potential answers to those questions. People with a sense of curiosity are more likely to come up with probing questions and explore.
When we are curious about something, we will likely research it to discover more, leading to new perspectives and insights.
5. Tolerance
For effective problem solving, you need to be open to all viewpoints, regardless of whether those agree or disagree with yours. In order to make sound decisions, you must be able to understand and respect other opinions. It can be challenging, but it is essential.
Tolerance is crucial in critical thinking because it recognizes that no one can have all the answers and that different perspectives can be helpful.
6. Communication
Critical thinkers need effective communication skills for several reasons. First, it allows you to share ideas and solicit feedback from others. It is always useful to understand different perspectives, as we have already noted.
The next step is to reevaluate your beliefs after communicating and gathering information from various sources.
You should be unbiased at this stage because one of the problems with human thinking is that we tend to seek information that supports our current beliefs and reject information that contradicts them because of our confirmation bias.
The ability to communicate well allows critical thinkers to build relationships with others. They can come up with new ideas and solve problems by working together.
7. Active listening
Critical thinking ability needs active listening skills to fully understand what people say and come up with logical counterarguments.
Active listening is more than listening to what someone says. It means paying close attention to what’s said and body language when necessary. This means listening to both the facts and feelings behind the message.
It also involves paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues. These cues help make logical connections between statements and the emotions associated with them. You always need to dig deeper than the face value of a statement.
How to be a critical thinker | 4-step process
A critical thinker can incorporate the following decision making process to resolve issues.
- Clarify the problem or goal
- Determine your criteria
- Consider available solutions
- Implement a solution
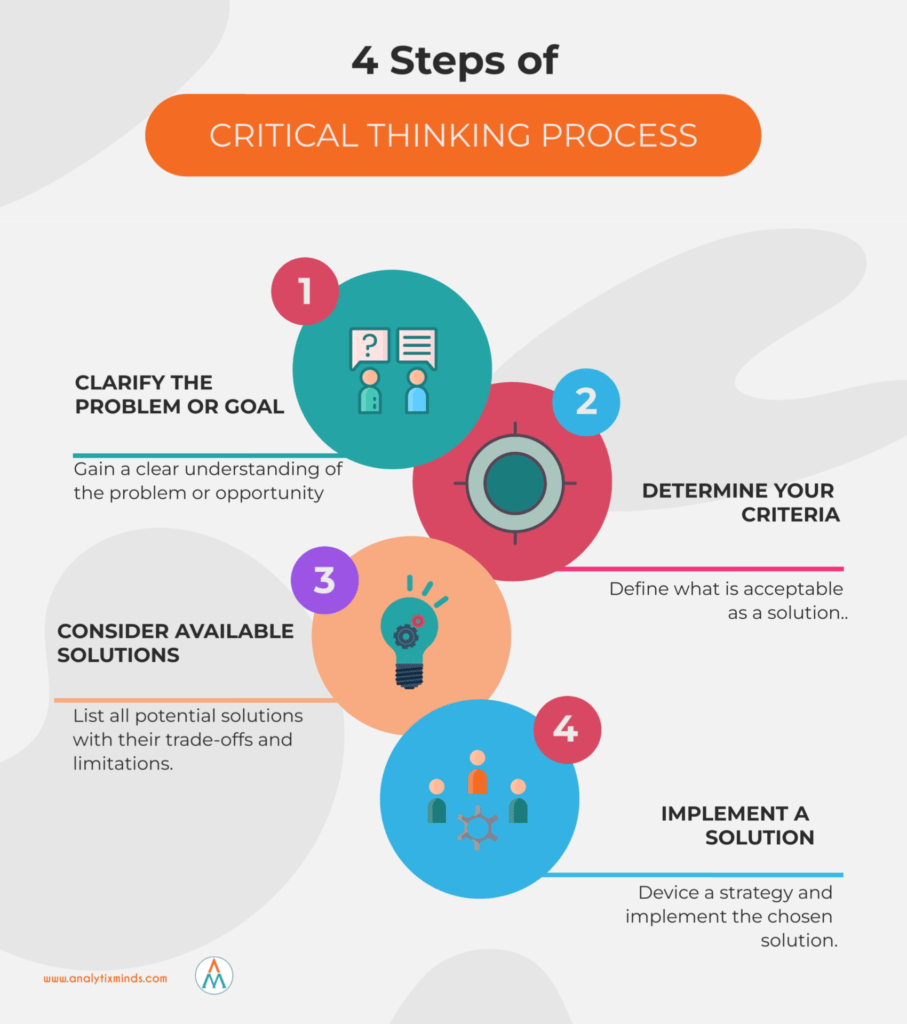
Here’s a breakdown of these steps.
Step 1 – Clarify the problem or goal
Here are a couple of questions to ask yourself.
- Can you explain the problem?
- What is the outcome we would accept?
In identifying your goals in resolving an issue, you may ask yourself questions such as;
- What would happen if we did not solve this problem?
- What would we do differently if we did solve this problem?
A clear understanding of the problem is critical because if you cannot identify the key elements and understand how they interrelate, you will be unable to find the best solution. This step is crucial to find the best solution.
Step 2 – Determine your criteria
A criterion defines what is acceptable as a solution. It could be something measurable metrics, requirements, and strategies that can be used to determine what constitutes a reasonable solution.
You must consider factors such as pay, career growth potential, working hours, location, and job security when changing jobs. You can make the best decision by analyzing your opportunities based on each criterion.
Step 3 – Create an inventory of existing solutions
After you’ve defined the problem and the criteria, you can look into possible solutions. This requires you to look at the problem from a fresh perspective.
When you have a list of potential solutions, you need to review each one of them and decide whether it will help your problem solving effort. Some options will help solve the problem. Some might seem like they’d help but might cause more problems than they solve, so there are trade-offs.
Suppose you want to reduce long lines at the cashier, so you decide whether or not to introduce an automated checkout system. It would probably reduce wait times, but if the checkout machines aren’t user-friendly, it will frustrate customers.
Basically, you draw conclusions and go ahead with the selected solution.
Step 4 – Implement a solution
After you have decided on a solution, you must devise a strategy for its implementation. Unfortunately, many excellent strategies fail because people refuse to put in the effort required to make them successful.
The ability to estimate the probability of success is the most important critical thinking skill you need to develop the right strategy.
Critical thinking pitfalls
The critical thinking process can be tricky if you don’t know the common pitfalls. Here are some of them.
Making incorrect assumptions
Assumptions are ideas that we believe to be true. When we make them, we accept that something is true without having enough evidence or experience to support that idea. You cannot take anything at face value without rigorous analysis.
Consequently, we make reasoning errors when we make wrong assumptions. Whenever you are thinking critically, it is crucial to gain as much information as possible before making assumptions.
When new information is acquired, assumptions need to be revalidated. We should always provide evidence to support our assumptions and continuously question their validity.
Letting emotions get in the way
Emotional beliefs are not the same as knowledge or truth. A belief may be wrong even if most people accept it. It is more important to investigate the truth behind a belief than how strongly you feel about it. The reasons must be epistemic and grounded in factual information.
Epistemic reasoning is the process of forming beliefs based on what is known and verified by scientific knowledge. This ensures that scientific belief is based on fact rather than opinion.
Confusing correlation with causation
A critical thinker should be able to distinguish between these two terms. Correlation refers to the degree to which two things are related. A change in one variable always affects the other.
Causation is when something causes another thing to happen. The correlation between two things doesn’t mean one thing causes the other.
It is common for correlation to be mistaken for causation. For example, it can appear that one thing causes another when two things are correlated. Critical thinkers need to know when a correlation isn’t causation to avoid making false assumptions.
Avoiding confirmation bias
Confirmation bias occurs when we overvalue evidence that supports our existing beliefs while downplaying or ignoring evidence that contradicts those beliefs. As a result, we can become confused, make poor decisions, and hold onto false beliefs despite contradictory evidence.
This error is known to critical thinkers. So, they strive to consider all the evidence supporting and against their beliefs. As a result, we can make more informed decisions, and if new evidence contradicts our existing beliefs, we can revise their beliefs.
Getting trapped in traditional beliefs
People mistakenly believe something simply because it is traditional. As critical thinkers, we need to examine why we hold those beliefs. The goal isn’t to abandon all conventional beliefs but to critically examine them to ensure they remain valid.
The fact that something has been around for a long time does not necessarily suggest that it is true. Good critical thinking requires questioning our beliefs and considering other perspectives.
Concluding thoughts
In everyday life, critical thinking is one of the intellectual tools that can help make an informed decision on any problem. You have to come up with an intellectually disciplined process. With the vast amount of information available at our fingertips, it’s more important than ever to discern the relevant information from the irrelevant.
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution to improve your critical thinking skills, there are some key concepts critical thinkers need to consider. Your ability to see the world around you more clearly can be improved by honing your observation, logical reasoning, and inference skills.
How do you improve critical thinking skills? We discussed some general tips to help you become a better critical thinker. But, first, ask questions and look at things from multiple perspectives.
Second, think logically and rationally; don’t let emotions cloud your judgment. Third, constantly challenge your own beliefs and assumptions, and be willing to change your mind when new evidence is presented. Finally, always be open-minded and tolerant of other viewpoints, even if you disagree.
Related articles
Successful problem solving also requires strategic thinking. Read about the role of strategic thinking skills in your decision making.
